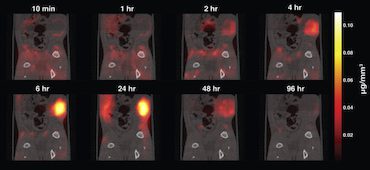
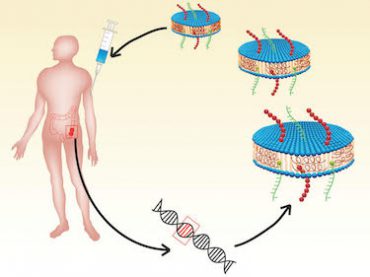
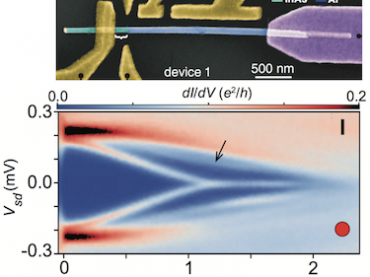
Magnetic particle imaging for early cancer detection
Magnetic particle imaging is a new, up-and-coming, safe and highly sensitive tracer imaging technique that works by detecting superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with high image contrast (that is, no background tissue signal). The technique, which does not use any ionizing radiation, can be used to image anywhere inside the body, which means that it could […]