ramjitti
Superconducting quantum-dot turnstile singles out electrons
A metallic quantum dot sandwiched between two superconductors – which functions as an electronic turnstile, only permitting one electron through at a time –
ramjitti
May 17, 2016Photoactive pixels switch on and off
Thanks to photocurrent spectral atomic force microscopy (PCS-AFM), researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) say they have been able to observe photoactive pixels switching on and off in a heterostructure made of two different 2D materials. The technique might help in the design of new electronic and optoelectronic devices based on these atomically […]
ramjitti
May 17, 2016Photonic gyroids mimic butterfly wings
Using a technique called optical two-beam super-resolution lithography, researchers in Australia have succeeded in making photonic “gyroid” nanostructures similar to those found in butterfly wings. The artificial structures, which outperform their natural counterpart in many ways, might be used in a variety of photonics and optics technologies…. http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/64982 Comparing an artificial and natural gyroid structure
ramjitti
May 17, 2016Collecting hot carriers in graphene superlattices
t least five “hot carriers” are produced for every photon absorbed by superlattices made from graphene and boron nitride. This new result from researchers in New York, Tallahassee and Seattle, means that the carbon sheet could be used to make flexible optoelectronics devices such as ultrafast and highly efficient photodetectors and solar cells…. http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/64988 Moiré […]
ramjitti
May 17, 2016Analysing ‘3D graphene’
Researchers in Australia and Singapore are the first to have measured the electronic properties of topological Dirac semimetal thin films, which are 3D analogues of graphene. These films, made from sodium bismuth, have high charge carrier mobilities and could be used to make new electronic devices like topological transistors…….. http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/64999 Na3Bi thin films
ramjitti
May 17, 2016ramjitti
May 16, 2016ramjitti
May 11, 2016ramjitti
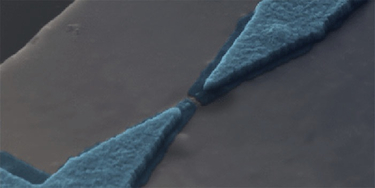
May 7, 2016The single-atom engine that could
Physicists in Germany have taken mechanical miniaturization to the ultimate limit by producing a heat engine – one of the key inventions of classical thermodynamics – made of only one atom, and have measured its output
ramjitti
April 26, 2016E-skin lights up in many colours
A new ultrathin and ultraflexible coating that can be made into an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display for use as electronic skin, or e-skin, has been developed by researchers at the University of Tokyo. Once applied to the skin, the coating can measure blood oxygen levels and heart rates……… http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/64708 Ultra-thin electronic skin
ramjitti
April 26, 2016Patterned liquid crystals guide light through planar lens
A new way to control light using liquid crystals has been developed by researchers in Japan, who believe that their method offers many of the advantages of an artificial “metasurface” while being much easier to fabricate on an industrial scale. Among other applications, the researchers believe the work could be useful for the production of […]
ramjitti
April 26, 2016Ball-milled coal for nanoelectronics
A new technique to make thin films from suspensions of ball-milled coal has been developed by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The films, which retain the rich carbon chemistry of the starting coals, could be used to fabricate a range of nanoelectronics devices, including transistors, photovoltaics and battery anodes…. http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/64744 Making organic […]
ramjitti
April 26, 2016Carbon nanotubes light up on photonic chips
A single carbon nanotube has been used as a scalable and tunable light source and integrated into a nanoscale waveguide by researchers in Germany. The nanotubes are part of a photonic-crystal waveguide that converts electric signals into light. The researchers hope their work could advance the field of optoelectronics and help to produce faster computer […]
ramjitti
April 26, 2016Quantum-dot barcodes for diagnosing disease
Researchers at the University of Toronto and University Health Network in Canada have performed the first full clinical study showing that quantum-dot barcodes can be used to diagnose patients infected with the hepatitis B virus. The new work is a “critical step” to translating quantum-dot technology into medical applications, they say…. http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/64760 In the lab
ramjitti
April 26, 2016ramjitti
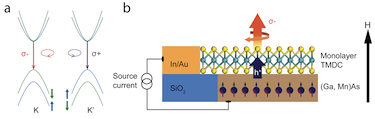
April 23, 2016Electrically controlling valley carriers in 2D materials
Researchers in the US and China are reporting on a new way to electrically generate and control valley carriers in 2D materials.
ramjitti
April 21, 2016Theory consultancy catalyses big business opportunities
Nanolayers Research Computing aims to bridge the gap between academic physics and real world products. The company was founded in 2015 to provide consultancy in modelling and simulations rather than “black box” software development, and business opportunities are already piling in…….. http://nanotechweb.org/cws/article/tech/64525 Work on “CritCat” in June 2016
ramjitti
April 21, 2016DNA machine controls chemical reactions
Researchers at the universities of Oxford and Warwick in the UK have used a DNA nanomachine to control a set of chemical reactions in a sort of nanoscale manufacturing line that they have dubbed a molecular assembler. The reactions in question normally occur very slowly, but the DNA molecules help to bring the reactants closer […]
ramjitti
April 21, 2016Nanocrystal inks used to build flexible transistors
A high-quality, flexible transistor, made entirely from colloidal nanocrystals, has been developed by a team in the US. By sequentially depositing their components in the form of nanocrystal “inks,” the researchers could make transistors using standard industrial methods, without the need for high-temperature, high-vacuum specialist equipment. The work can be scaled up, so it could […]
ramjitti
April 21, 2016Diamond quantum bit is controlled using light and sound
Physicists in the US are the first to use a combination of light and sound to control the state of a diamond-based quantum bit (qubit) of information. The team used a laser pulse and a sound wave to modify the energy state of an electron in a nitrogen vacancy (NV) centre in diamond. According to […]