
NANOENCAPSULATION AND BIODELIVERY
SYSTEMS RESEARCH GROUP
Nanoencapsulation and Biodelivery Systems Research Group (NCBS) at NANOTEC’s mission is to design and synthesis of nano-scaled delivery platforms with improved multi-performance characteristics and pharmaceutical actions using a combination of various strategies. NCAP has major research efforts in development of advanced nanocarriers for natural products, pharmaceuticals or bioactive substances. We focus not only on bio-inspired/biomimicking nanocarriers but we are also interested in utilizing material specific properties to create innovative nanocarriers with controllable properties such as bioadhesive or stimuli-responsive nano-delivery systems. Correspondingly, we actively work on surface functionalization/modification for more precise systems, for example, nanoparticles for molecular/immuno-targeted therapy. Our expertise expands to green extraction and purification techniques to acquire new substances from natural products. We also have systemic biological activity screening to identify possible applications for those.
What We Do
- Engineer advanced nanocarriers for natural extracts, drugs, and bioactives. Platforms include lipid-based systems, polymeric nanoparticles, and hybrid/bio-inspired carriers that can be tuned for size, charge, permeability, and interfacial behavior.
- Create bio-inspired/biomimicking delivery systems. By taking cues from biological membranes and soft-matter assemblies, we develop carriers that are skin-mimetic, comfortable on application, and compatible with delicate actives.
- Develop stimuli-responsive and bioadhesive systems. Our formulations can respond to pH, temperature, enzymes, or light, and are designed to adhere to skin or mucosa when prolonged residence is advantageous.
- Apply surface functionalization/modification. We tailor nanoparticle surfaces with ligands or other chemistries to enable molecular/immuno-targeted therapy, improving localization and reducing unwanted exposure.
- Advance green extraction and purification. To access high-value compounds from botanical and natural resources, we employ environmentally considerate extraction/purification methods that preserve activity and minimize impurities before encapsulation.
- Screen biological activity systematically. Standardized bioactivity screening helps us identify promising applications, compare candidate carriers, and confirm that encapsulation preserves or enhances functional performance.
How We Work
Projects follow a clear R&D pathway: selection and purification of bioactives → carrier design and synthesis → physico-chemical characterization (size, morphology, charge, release) → surface and functional optimization → biological activity screening and relevant safety/compatibility checks → prototype formulations suited to topical, oral, or systemic delivery. The group collaborates with internal and external partners to move results toward application in cosmeceuticals, nutricosmetics, human healthcare, and animal healthcare.
Our aim is to translate fundamental nanoencapsulation principles into practical nano-actives and formulations that withstand real-world processing, storage, and use—while generating clear, reproducible data that partners can rely on.
Research Teams
The Nanoencapsulation (NCAP) Research Group is organized into two specialized teams that deepen and expand its scope of research:
1. Nanolife & Cosmeceuticals Research Team (NLC)
The NLC team develops nano-scaled delivery platforms and green-made active ingredients for applications in personal care and household products. Their work emphasizes precision delivery, controlled release, and bio-inspired nanocarriers tailored for skin, hair, oral, and hygiene applications.
Focus areas include:
- Green extraction of bioactives from Thailand’s biodiversity, including black ginger (กระชายดำ) and moringa (มะรุม).
- Green synthesis of bioactive small molecules using environmentally friendly approaches.
- Topical solutions for dermatitis and inflammatory conditions, combining anti-inflammatory release with bioadhesive carriers.
- Platform technologies such as second-skin films and microneedle patches for transdermal delivery.
- Nutricosmetics and household products where controlled delivery enhances performance.
The NLC team translates lab-scale ideas into scalable prototypes compatible with industrial manufacturing, bridging nanoscience and consumer-ready products.
2. Nanomedicine & Veterinary Research Team (NMV)
The NMV team applies drug delivery systems for encapsulation, controlled release, and targeted delivery of herbs, pharmaceuticals, and biopharmaceuticals. Their work spans both human healthcare and veterinary applications, addressing unmet needs in prevention and treatment.
Research directions include:
- Active targeting systems for brain degenerative diseases.
- Liposomes and exosomes as advanced carriers for drug and biologic delivery.
- Targeted liposomal delivery for anti-cancer applications (e.g., cervical cancer).
- Thermo-responsive bacteriophage nanocarriers for gene therapy in gastrointestinal diseases and infections.
- Hyaluronic acid-coated gold nanorods for cartilage regeneration (chondrogenesis).
- Antibiotic encapsulation and alternatives to address resistance.
- Mucoadhesive vaccines for aquaculture species (fish).
- Non-surgical sterilization methods for animal health management.
By combining nanomedicine with veterinary science, NMV delivers innovations that enhance health outcomes, reduce reliance on antibiotics, and create safer, more effective therapeutic options.
Flagship Case
Below are representative examples that illustrate NCAP’s approach—from problem framing through nano-solution and validation.

- Thai Herbal Hair Nano-Active (ใบหมี่ + บัวบก)
Challenge. Hair-care actives from traditional botanicals often suffer from instability (color/odor drift, oxidation) and limited delivery to the follicle.
NCAP solution. We combined the strengths of ใบหมี่ (Bai-Mi) for hair-root support with บัวบก (Centella asiatica) for anti-inflammatory action, then encapsulated the extracts in nanoparticles to enhance stability and moderate release on the scalp.
What the data show. In laboratory studies, the nano-formulation stimulated human hair-follicle cell proliferation and reduced inflammatory markers. Dermatologist-supervised single patch tests indicated non-irritation. A clinical observation in volunteers with chronic hair-loss reported improvement in hair growth (≈5–8%) after continuous use over three months.
Use. The ingredient is formulation-friendly for haircare products, with a recommended usage range of ~0.5–5%.
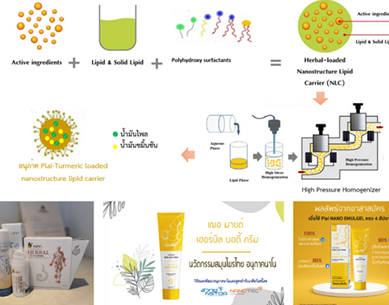
2. Herbal Emulgel for Muscle and Joint Discomfort (ไพล + ขมิ้นชัน)
Challenge. Consumers increasingly seek nature-derived relief without harsh counter-irritants, yet essential oils and herbal actives can be volatile or irritating.
NCAP solution. We developed an emulgel in which essential oils and herbal extracts are encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles, supporting fast sensation of relief and a sustained cooling effect while maintaining a non-greasy feel.
Outcome. Encapsulation improved dermal compatibility and delivery. The technology has been licensed to private companies for commercial use, reflecting its scalability and market fit.

3. Q-Mas: Nano-Herbal Cream for Subclinical Mastitis in Cows
Challenge. Subclinical mastitis reduces milk quality and can lead to antibiotic use; producers seek supportive, non-antibiotic approaches.
NCAP solution. A nano-herbal moisturizing cream was designed to deliver anti-inflammatory activity to the mammary gland. Nanoencapsulation improves stability and residence, helping actives reach the intended tissue and act over longer durations.
Outcome. Field use in affected dairy cows was associated with a reduction in somatic cell count, a milk-quality indicator linked to udder health. The product emerged from multidisciplinary collaboration across nanomedicine and veterinary research teams.

4. Fenugreek Liponiosome Serum
Challenge. Fenugreek seed extracts are rich in bioactive flavonoids (e.g., rutin) but are chemically unstable, complicating cosmetic use.
NCAP solution. We encapsulated fenugreek extract in liponiosomes, a hybrid lipid carrier, to increase stability and preserve activity. The extract-loaded carriers were formulated into a facial serum.
Outcome. In-vitro anti-collagenase testing supported anti-aging relevance. Evaluation with >100 volunteers indicated the product was non-irritating, with improvements in skin elasticity and moisturization.
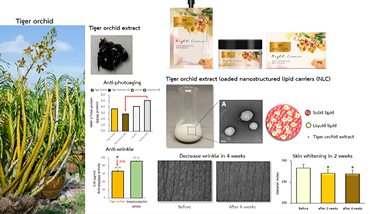
5. Tiger Orchid (Grammatophyllum speciosum) NLC Anti-Wrinkle Cream
Challenge. Tiger orchid extract contains phenolic glycosides with anti-oxidant and anti-photoaging potential, yet it requires solubility and stability enhancement for topical use.
NCAP solution. The extract was incorporated into nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) to improve solubility, spreadability, stability, and skin penetration.
Outcome. In an in-vivo evaluation with 31 Asian volunteers (35–55 years), the cream was non-irritating, reduced wrinkle parameters within 4 weeks, and showed visible skin brightening within 2 weeks.
These flagship cases exemplify NCAP’s mission: converting sensitive bioactives into dependable nano-actives through encapsulation, surface engineering, and systematic biological assessment.



